In this post, we’ll explore several effective ways to enhance the efficiency of phosphorus fertilizers, making them more effective for crops and beneficial for sustainable agricultural practices.
1. Improving Phosphorus Availability in Soil
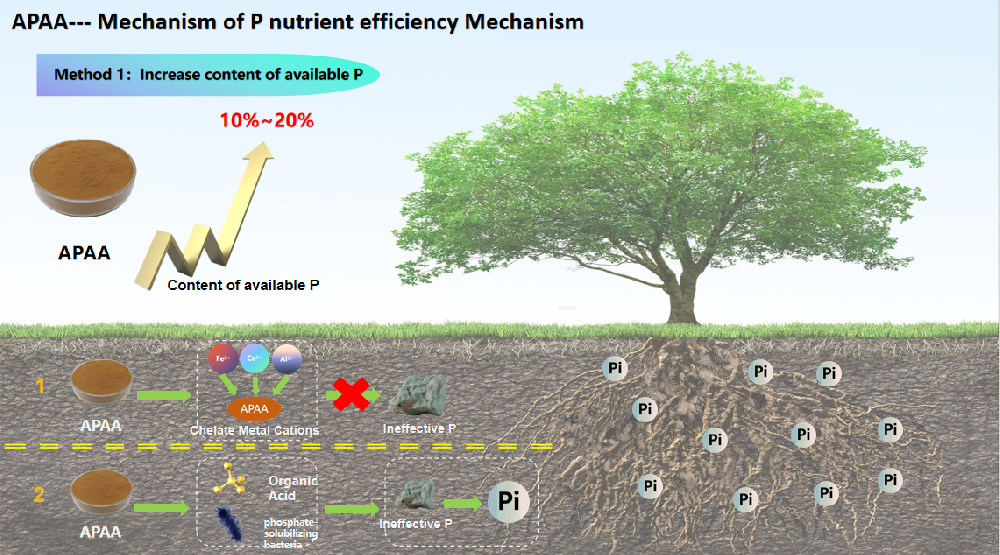
One of the most common reasons for low phosphorus uptake by plants is the unavailability of phosphorus in the soil. Phosphorus can become chemically fixed in soil through interactions with iron, aluminum, or calcium, making it unavailable to plants. To address this, soil amendments and biostimulants can be used to unlock and increase the availability of soil phosphorus.
By using certain products, like Seawinner APAA, which is designed to enhance phosphorus uptake, it's possible to improve the availability of fixed phosphorus in the soil. APAA works by activating soil microorganisms that help release bound phosphorus and improve its accessibility for plant roots.
2. Encouraging Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria
Another effective strategy to boost phosphorus efficiency is to promote the activity of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria[1] in the soil. These beneficial microorganisms help break down organic and inorganic phosphorus compounds into soluble forms that can be readily absorbed by plant roots. Incorporating biostimulants like Seawinner APAA can stimulate the activity of these bacteria, further enhancing phosphorus release and utilization.
3. Optimizing Fertilizer Application
Applying phosphorus fertilizers in a way that maximizes their uptake is essential. Broadcasting or top-dressing fertilizers may lead to phosphorus being immobilized in the soil or washed away by rain. Instead, banding fertilizers close to the root zone can significantly increase the efficiency of phosphorus absorption. Moreover, adjusting the application rate based on soil test results helps ensure that plants receive just the right amount of phosphorus needed for optimal growth.
Additionally, the use of products like Seawnner APAA can be integrated into fertilization practices, improving phosphorus fertilizer's effectiveness by increasing phosphorus solubility and reducing leaching.
4. Enhancing Root System Development
Plants with more developed root systems can better access phosphorus and other nutrients in the soil. Root growth is essential for efficient nutrient uptake, particularly in phosphorus-poor soils. Certain biostimulants and soil conditioners, like APAA, promote root growth by stimulating the secretion of organic acids and enhancing root system development. With a more extensive and vigorous root network, crops can explore a larger volume of soil, improving their ability to absorb phosphorus and other essential nutrients.
5. Sustainable Farming Practices
As the agricultural industry moves toward more sustainable practices, enhancing phosphorus efficiency is crucial. Reducing the loss of phosphorus through runoff, leaching, and fixation is key to protecting the environment and ensuring long-term soil health. APAA, being derived from marine biotechnology, not only boosts phosphorus uptake but also helps reduce nutrient loss, supporting more sustainable and eco-friendly farming practices.
Conclusion
Enhancing phosphorus fertilizer efficiency is vital for improving crop yields while reducing environmental impact. By optimizing phosphorus availability, encouraging beneficial soil microorganisms, promoting root development, and using advanced products like APAA, farmers can make better use of the phosphorus in their soils, ensuring healthy crops and sustainable farming practices.
With products like Seawnner APAA, which activate soil microbes, enhance phosphorus uptake, and improve root growth, achieving better phosphorus utilization is now more accessible than ever before. As we continue to develop innovative solutions in agriculture, the use of biostimulants like APAA presents a promising way to enhance soil fertility and boost crop production.